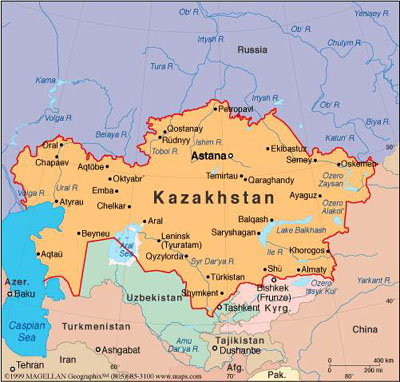
The Republic of Kazakhstan
The Republic of Kazakhstan is situated at the turn of the two continents - Europe and Asia, between the 45th and 87th degrees of longitude East and between the 40th and 55th degrees of latitude North. The geographical center of the European-Asian subcontinent is located in Kazakhstan (at the intersection of the meridian and the 50 parallel) - in the epicenter of the former Semipalatinsk nuclear test grounds. Kazakhstan occupies the territory of 2724.9 thousand square km (1048.3 thousand square miles) and is located to the east of the Caspian Sea and THE Volga's plains of to the mountainous Altay, from the foothills of the Tien-Shan in the South and South-East to the West-Siberian lowlands in the North. The length of its territory from west to east is more than 3,000 km (1,150 miles), from south to north - 1,700 km (650 miles).
Kazakhstan takes the ninth place in the world for its territory, i.?. it is among the ten largest states of the world - after Russia, Canada, China, the USA, Brazil, Australia, India and Argentina. Kazakhstan borders at the east, north and north -east with Russia (length of the borders is 6,477 km), at the south - with countries of Central Asia - Uzbekistan (2,300 km), Kyrgyzstan (980 km) and Turkmenistan (380 km), at the south -east - with China (1,460 km). Total length of Kazakhstan borders is about 12.2 thousand km, including 600 km along the Caspian Sea (at the west).
Today the challenge of global climate change is one of the most urgent world problems, and it is important for all countries of the world community: for industrialized countries - because of the high level of energy use in all sectors of economy, and, consequently, of greenhouse gases emissions into the atmosphere; for countries with transitional economy that are, at first sight, not interested in activities on climate change prevention, but in reality they depend on them; for developing countries, which need to increase production volumes and which face the dilemma- whether they should participate in the global process of greenhouse gases reduction through establishment of their concentration control and introduction of effective technologies and less energy-consuming productions.
A very vulnerable environment characterizes the Republic of Kazakhstan: many types of landscape are presented in the country - from dry subtropics and deserts to mountainous glaciers. Many unique inland water reservoirs are located on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan - seas and lakes the Caspian, Aral, Balhash. Possessing unique stocks of natural resources (oil, gas, ferrous and non-ferrous metals, etc.), Kazakhstan in the times of the USSR was a raw materials appendix of the country, natural resources were often extracted without the regard of the negative impact upon environment and human health. The population of Kazakhstan really felt and continues to feel on themselves and on their health fatal consequences of environmental catastrophes, the reason of which is antropogenic activities. The development of virgin lands resulted in ploughing up of enormous territories of the country, intensive irrational development of irrigable farming in the basins of the rivers Amu Darya and Syr Darya - in the tragedy of the Aral Sea, rise of water level in the Caspian Sea - in flooding of the oil wells and oil-rigs and threat to lose biodiversity of the Caspian region. Significant territories of the country for the period of 1949 to 1991 were, and in some places still remain to be, under the pressing of the military industrial sector. Kazakhstan has suffered some the tests of nuclear weapons (Semipalatinsk and Azgyr), of military equipment and machines (Yemba, Sary-Shagan, Kapustin Yar), space tests are still carried out (Baikonur). Even today it is difficult to evaluate and calculate the damage caused on environment, agriculture, economy and human health of Kazakhstan by the irrational and cruel attitude to nature. These examples is only a small part of the ones that can be used to model and give the idea about the possible, even more serious consequences that will appear as a result of global climate change.
|